The research team led by Professor Guo Zhiguang from School of Materials Science and Engineering Hubei University, has published their latest research paper in Small, titled Ultraslippery Surface for Efficient Fog Harvesting and Anti-Icing/Fouling. Zhang Huayang, postgraduate student from School of Materials Science and Engineering Hubei University, is the first author, Dr. Xie Shangzhen and Prof. Guo Zhiguang are the corresponding authors of the paper.
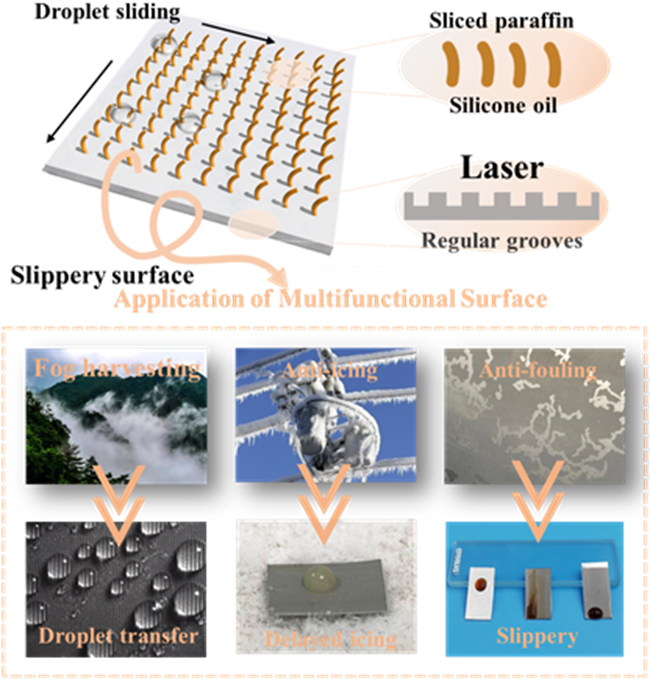
The conventional Slippery Liquid Infused Porous Surface (SLIPS) encounters challenges such as silicone oil leakage and complex manufacturing of rough substrate structures. Thus, it is crucial to develop a lubricant that is highly adaptable and less prone to loss for surface structures; a temperature-controlled method of infusing oleogel into a superhydrophobic surface (SHS) is presented in this paper. This approach draws inspiration from the characteristics of Nepenthes pitcher plant structures, albeit without the need for intricate pore-making or nanowire structures. It is demonstrated that this resulting surface has exceptional fog harvesting capability, with a fog harvesting efficiency of 0.3222 g cm−2 min−1, which is twice as high as that of the laser aluminum (Al) sheet (0.1553 g cm−2 min−1). Moreover, the surface exhibits remarkable anti-icing properties, significantly prolonging the icing time by 21-fold compared to the pure Al sheet while maintaining a minimal ice adhesion force of only 0.16 N. Additionally, the surface showcases excellent antifouling performance, because contaminated droplets readily slide off without leaving residue. The environmentally friendly and straightforward preparation process ensures that it is suitable for large-scale industrial applications.
Professor Guo Zhiguang has made headway through research on performance and mechanism in fields of oil-water separation, anti-icing and de-icing, fog harvesting, and bubble manipulation by regulating the wettability of material surfaces. He has obtained key projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Outstanding Youth Science Foundation, and has published over 520 academic papers with more than 21,000 citations, and a H-factor of 76, two monographs respectively in English and Chinese. Dr. Xie Shangzhen’research primarily revolves around biomimetic surfacefor atmospheric water harvesting, oil-water separation, and passive thermal management in new energy devices. She has published over 10 academic papers in renowned journals, and has awarded the title of Chutian Scholar in Hubei Province, and has been sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China for Youth Science Fund.
Link for the research article: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202405875